Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shobu, Takahisa; Mizuki, Junichiro; Suzuki, Kenji*; Akiniwa, Yoshiaki*; Tanaka, Keisuke*
JSME International Journal, Series A, 49(3), p.376 - 381, 2006/07
The surface aberration effect in the strain scanning method with a Ge analyzer was examined using high-energy X-rays from the undulator synchrotron source. The use of a Ge (111) analyzer showed remarkable reduction of the surface aberration effect. However, there still existed the surface aberration for the very-near surface region from the surface to the depth of 50 micro meter. A correction method was proposed by taking into account of the effects of the divergence of the Ge analyzer, the mis-setting of the analyzer and the X-ray attenuation. The proposed correction method was very useful for eliminating the surface aberration effect. The correction method enables a high space-resolutive evaluation of the subsurface stress distribution. The method was successfully applied to the determination of the residual stress distribution of the shot-peened steel.
Watanabe, Tadashi; Kondo, Masaya
JSME International Journal, Series B, 49(2), p.296 - 301, 2006/05
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Akemi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 49(2), p.360 - 367, 2006/05
Since it is generally difficult to predict the occurrence of natural disasters such as earthquakes, a performance management system that always maintains the safety and functionalities of structures is required, especially for critical ones like nuclear power plants. In order to realize such a system, it is becoming important to carry out modeling procedures and analyses in detail to better understand the real phenomena. The aim of our research is to solve the dynamic behavior, especially the wave propagation phenomena, of piping systems in nuclear power plants which are complicated assemblages of parts. The spectral element method is adopted in this work and the formulation considering a shear deformation independently for a frame element is described. The Timoshenko beam theory is introduced for the purpose of this formulation. Moreover, the validity of the presented element will be described through comparisons made with the conventional beam element by showing the numerical example using the steel pipe actually used as the piping in HTTR, JAEA.
Nakagiri, Toshio; Kase, Takeshi; Kato, Shoichi; Aoto, Kazumi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 49(2), p.302 - 308, 2006/05
A new thermo-chemical and electrolytic hybrid hydrogen production system in lower temperature range is newly proposed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to realize the hydrogen production from water by using the heat generation of sodium cooled Fast Breader Reactor (FBR). The system is based on sulfuric acid (H SO
SO ) synthesis and decomposition process developed earlier (Westinghouse process), and sulfur trioxide (SO
) synthesis and decomposition process developed earlier (Westinghouse process), and sulfur trioxide (SO ) decomposition process is facilitated by electrolysis with ionic oxygen conductive solid electrolyte to reduce the operation temperature 200-300
) decomposition process is facilitated by electrolysis with ionic oxygen conductive solid electrolyte to reduce the operation temperature 200-300  C lower than Westinghouse process. SO
C lower than Westinghouse process. SO decomposition was confirmed experimentally, and theoretical thermal efficiency was evaluated. Furthermore, hydrogen production experiments to substantiate the whole process were performed. Stable hydrogen and oxygen production were observed in the experiments, and maximum duration of the experiments was about 5 hours.
decomposition was confirmed experimentally, and theoretical thermal efficiency was evaluated. Furthermore, hydrogen production experiments to substantiate the whole process were performed. Stable hydrogen and oxygen production were observed in the experiments, and maximum duration of the experiments was about 5 hours.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Naoe, Takashi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Date, Hidefumi*; Ikeda, Yujiro
JSME International Journal, Series A, 48(4), p.234 - 239, 2005/10
Mercury target will be installed at the material science and life facility in J-PARC, which will promote innovative science. The mercury target will be subjected to the pressure wave caused by proton bombarding in the mercury. The pressure wave propagation induces the cavitation in mercury that imposes localized impact damage on the target vessel. The impact erosion is a critical issue to decide the lifetime of target. An electromagnetic impact testing machine, MIMTM, was developed to reproduce the localized impact erosion damage and evaluate the damage formation. Additionally, droplet impact analyses were carried out to investigate the correlation between isolate pit profile and micro-jet velocity. We confirmed that the value of depth/radius was applicable to estimate micro-jet velocity, and the velocity at 560 W in MIMTM equivalent to 1MW proton beam injection was 300 m/s approximately.
Naoe, Takashi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Naito, Akira*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Yujiro; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*
JSME International Journal, Series A, 48(4), p.280 - 285, 2005/10
Target vessel materials used in spallation neutron source will be exposed to proton and neutron irradiation and mercury immersion environments. In order to evaluate the surface degradation of the vessel candidate materials due to such environment, the triple-ion beam irradiation taking the spallation reaction into account and mercury immersion tests were carried out. Mechanical properties of the gradient surface layer ware evaluated by the inverse analysis with multi-layer model that considers distribution of surface characteristic was applied to the load and depth curves measured by using the instrumented indentation machine. Transmission electron microscopic observations ware performed to evaluate the changes of microstructure in irradiated surface layer using focused ion-beam cut micro-specimen. It was confirmed that the ductility loss is enhanced by the irradiation and mercury immersion, and simulated stress and strain curves of the ion-irradiated surface layer ware adequately in good agreement with the curves of experimental equivalent neutron-irradiated material.
Zherebtsov, S.*; Maekawa, Katsuhiro*; Hayashi, Terutake*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
JSME International Journal, Series A, 48(4), p.292 - 298, 2005/10
The effect of temperature on the structure and properties of the type 316 stainless steel alloyed with Al-Si has been reported in the present paper. It has been found that four different types of structure are formed in the alloyed zone depending on the temperature of the substrate. These structures differ from each other in phase composition, microhardness and relation to cracking. Hard, crack-free microstructures are formed at temperatures of about 350 and 750  C. Maintaining the temperature of the sample at 350
C. Maintaining the temperature of the sample at 350  C a uniform, crack-free layer with a high hardness is produced by laser alloying with an energy density of 0.76 W/mm
C a uniform, crack-free layer with a high hardness is produced by laser alloying with an energy density of 0.76 W/mm .
.
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Kimura, Hideo
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(4), p.761 - 767, 2004/11
In this paper, we show that a new numerical method, the Constrained Interpolation Profile - Basis Set (CIP-BS) method, can solve partial differential equations (PDEs) with high accuracy and can be a universal solver by presenting examples for the solutions of typical parabolic, hyperbolic, and elliptic equations. Here, we present the numerical errors caused by this method, and illustrate that the solutions by the CIP-BS method, in which fifth order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first and second order spatial derivatives, are highly refined compared to those by the CIP-BS
method, in which fifth order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first and second order spatial derivatives, are highly refined compared to those by the CIP-BS method, in which third order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first order spatial derivatives. The fact that this method can unambiguously solve PDEs with an one-to-one correspondence to analytical requirements is also shown for PDEs including singular functions like the Dirac delta function with Dirichet or Neumann boundary conditions. This method is straightforwardly applicable to PDEs describing complex physical and engineering problems.
method, in which third order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first order spatial derivatives. The fact that this method can unambiguously solve PDEs with an one-to-one correspondence to analytical requirements is also shown for PDEs including singular functions like the Dirac delta function with Dirichet or Neumann boundary conditions. This method is straightforwardly applicable to PDEs describing complex physical and engineering problems.
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Yabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(4), p.768 - 776, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Kudo, Kazuhiko*; Li, H.*; Li, B.-X.*; Saito, Jun*; Yamaguchi, Akira; Takata, Takashi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(3), p.631 - 636, 2004/08
A method to estimate complex refractive index of dielectric aerosols is developed. For the purpose, three-dimensional radiative transfer problem in an absorbing-scattering media is solved by the Monte Carlo method. The Mie.s scattering theory is used to handle particle scattering and absorption. Magnesium oxide aerosol, whose complex index of refraction is well known, is selected as the example of the dielectric aerosol. Magnesium is burnt to produce MgO aerosol and the transmission of the radiation from a black body furnace through the aerosol layer is measured. By comparing the analytical results of transmitted energy profile along the wall facing the emission resource, black body furnace, obtained for a wide range of the complex index of refraction, with the experimental results, it is shown that the value of the complex refractive index of the aerosol can be estimated.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.479 - 485, 2004/07
In the structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel, fracture toughness values are estimated by assuming that the radiation effect on fracture toughness is equivalent to that on Charpy properties. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the correlation between both properties especially on irradiation embrittlement. In this paper, we present the fracture toughness data obtained by applying the master curve approach that was adopted recently in the ASTM test method. Materials used in this study are five ASTM A533B class 1 steels and one weld metal. Neutron irradiation for Charpy-size specimens as well as standard Charpy-v specimens was carried out at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor. The shifts of the reference temperature on fracture toughness due to neutron irradiation are evaluated. Correlation between the fracture toughness reference temperature and Charpy transition temperature is established. Based on the correlation, the optimum test temperature for fracture toughness testing and the method to determine a lower bound fracture toughness curve are discussed.
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.486 - 493, 2004/07
The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAERI. This code can evaluate the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Based on the temperature and stress distributions in the vessel wall for four PTS sequences in a typical 3-loop PWR, parametric PFM analyses are performed using PASCAL on the variables such as pre-service inspection model, crack geometry, fracture toughness curve and irradiation embrittlement prediction equation. The results showed that the good perfomance inspection model had a significant effect on the fracture probability and reduced it by more than 3 orders of magnitude. The fracture probability calculated by the fracture toughness estimation method in Japan was about 2 orders of magnitude lower than that by the USA method. It was found that the treatment of a semi-elliptical crack in PASCAL reduced the conservatism in a conventional method that it is transformed into an infinite length crack.
Kikuchi, Kenji; Saito, Shigeru; Kurata, Yuji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Wakai, Eiichi; Umeno, Makoto*; Mizubayashi, Hiroshi*; Miura, Kuniaki*
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.332 - 339, 2004/05
Lead bismuth eutectic (LBE) is favored by spallation neutron sources and coolant in the sub-critical reactor at the accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS). Technical issues of ADS are material technology of how to compromise with flowing lead bismuth, high-energy proton accelerator technology and a sub-critical reactor system technology. This paper describes LBE technology developed at JAERI. First a scenario in order to realize the ADS is shown. The concept of spallation target test facility is introduced with a target design of thermo-fluid dynamics. Base data of flow rate and temperature of Pb-Bi during LBE circulation are described. The results of LBE loop operation under the flowing conditions of target design concept are reported. The stagnant corrosion tests were done to know the controlling parameters among the various steels. The tube-type oxygen sensor with having the solid electrolyte was studied. Cleaning techniques were developed to remove LBE from materials.
Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Katanishi, Shoji; Takada, Shoji; Takizuka, Takakazu; Yan, X.; Kosugiyama, Shinichi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.261 - 267, 2004/05
The GTHTR300 aiming at electric generation with its thermal efficiency of 46 % is a safe and economically competitive HTGR in 2010s. A helium gas turbine system connected with the reactor is designed based on existing technologies developed for fossil gas turbine systems. However, there are some uncertainties in performance of a helium gas compressor, electric magnetic bearings and control system. In order to confirm these technical uncertainties, a 1/3 scale model of the compressor and 1/3 scale magnetic bearings will be manufactured and tested in the simulated condition of the GTHTR300. This paper describes R&D plans focusing on the 1/3 scale compressor model test as well as unique design features of the GTHTR300.
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Tamai, Hidesada
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.323 - 331, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hidesada; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Akimoto, Hajime
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.293 - 298, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Akimoto, Hajime
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.299 - 305, 2004/05
Experimental research on critical power in tight lattice bundle that simulates the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been carried out in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The bundle consists one center rod and six peripheral rods. The 7 rods are arranged on a 14.3 mm equilateral triangular pitch. Each rod is 13 mm in outside diameter. An axial 12-step power distribution is employed to simulate the complicate heating condition in RMWR. Experiments are carried out under  = 100-1400 kg/m
= 100-1400 kg/m s,
s, 
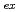 = 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.
= 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.
Watanabe, Tadashi; Ebihara, Kenichi
JSME International Journal, Series B, 45(3), p.600 - 606, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Kamide, Hideki; Kimura, Nobuyuki;
JSME International Journal, Series B, 45(3), p.577 - 585, 2002/08
None
Ioka, Ikuo; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Yonekawa, Minoru; Takada, Fumiki; Hoshiya, Taiji
JSME International Journal, Series A, 45(1), p.51 - 56, 2002/01
The low cycle creep-fatigue test with tensile strain hold of the austenitic stainless steel irradiated to 2dpa was carried out at 823K in vacuum. The applicability of creep-fatigue life prediction methods to the irradiated specimen was examined. The fatigue life on the irradiated specimen without tensile strain hold time was reduced by a factor of 2-5 in comparison with the unirradiated specimen. The fraction of intergranular fracture increased with increasing strain hold time. The decline in fatigue life of the irradiated specimen with tensile strain hold was almost equal to that of the unirradiated specimen. For the irradiated specimen, the time fraction damage rule trends to yield unsafe estimated lives and the ductility exhaustion damage rule trends to yield generous results. However, all of data were predicted within a factor of three on life by the linear damage rule.